Preclinical study of proliferative diabetic retinopathy hypoxia-induced morphological, biomechanical, compositional changes in erythrocytes retinal endothelial cells
- Publication Date: 2019-12-23
| Execution Methods | In biology and chemistry Methods: NƐ-carboxymethyllysine (CML) and inflammatory cytokines levels in human sera and in several diabetic murine models were detected by ELISA, while liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis (LC/M/SMS)) was used for diabetic subjects and animal whole eye tissues. The CML and specific targeting protein Tpl2 expressions on the retinal cells were determined by immunofluorescence. Intra-vitreal injection of pharmacological inhibitor or neutralizing antibody was used in a diabetic rat model. Retinal leukostasis, optical coherence tomography, and H and E staining were used to observe pathologic features. In physical analysis, we added new approach method by atomic force microscope(AFM). The erythrocytes by CML treated cells would be adopted for testing. |
| Performance Evaluation | 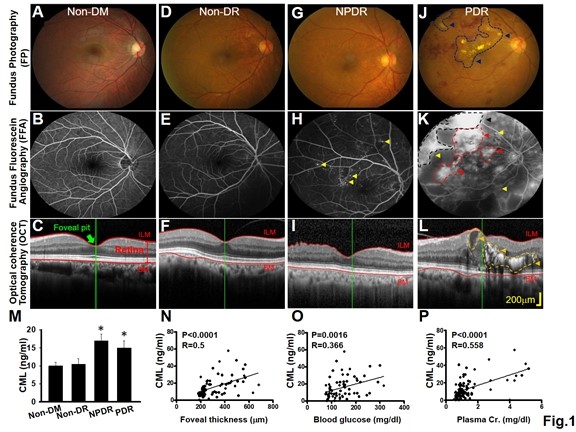 Figure 1. The clinical severity of DR positively correlated with serum CML level. 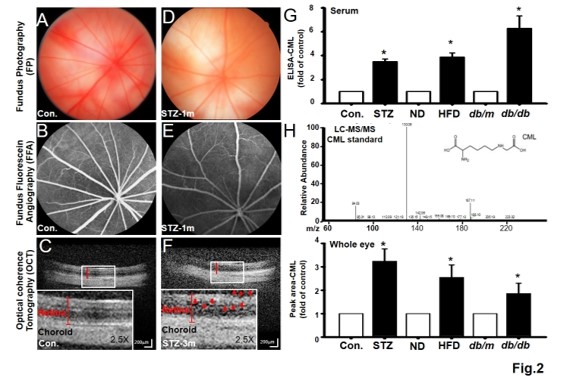 Figure 2. Retinal lesions of DR-like animal models all correlated with CML levels in serum and eye tissue. 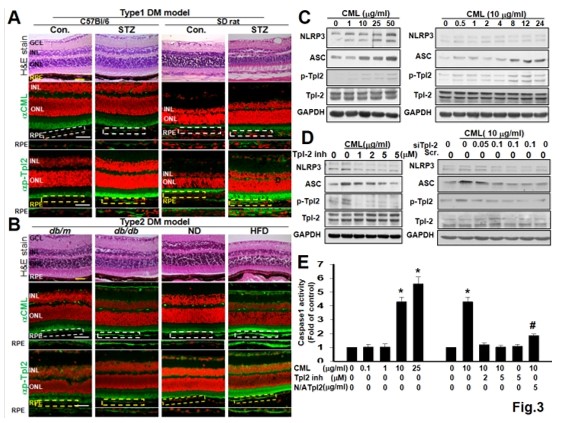 Figure 3. Both CML and p-Tpl2 expressions were enhanced in retinal cells of T1DM and T2DM animal models. 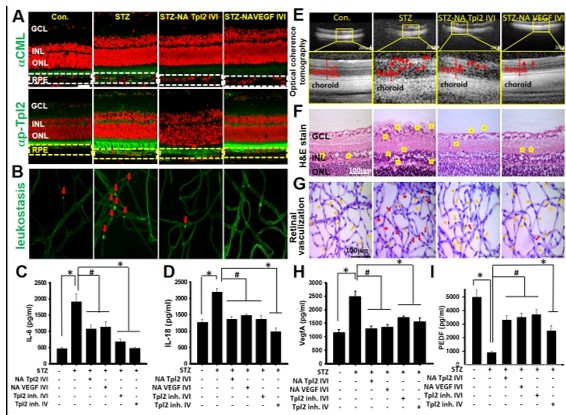 Figure 4. Intra-vitreal injection (IVI) of NA Tpl2 or NA VEGF effectively suppressed retinal inflammation and retinal neovascularization in STZ-induced diabetic rats. 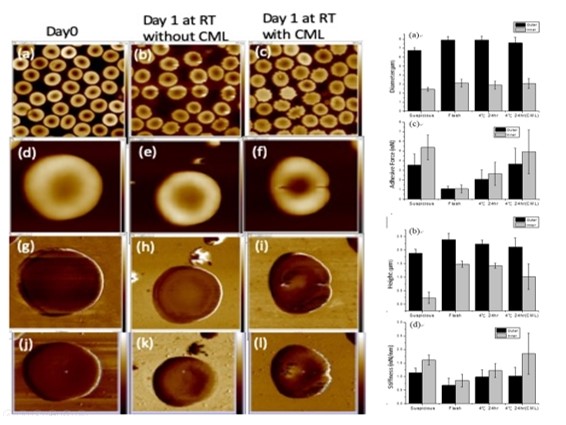 Fig.5 AFM topography and the dimension analysis. Left panel presented (a-f) along with adhesion images (g-i), stiffness(j-l) images of flash and CML treated RBCs. Right panel shown the dimension analysis in size(a) and height(b), the adhesion(c) and stiffness(d) of flash, CML treated and suspicious RBCs. |
| Conclusion & Suggestion | Conclusion: We suggest that CML increased in blood from patients on destroy cell membrane function and is thus a potential biomarker of oxidative damage in these patients. Moreover, CML may play a pathogenic role in the development of microvascular complication. Suggestion: Both Medical-biology study and LCMSMS study cooperated for a long time and stably publish in serial work. In the study we added Atomic force microscopy (AFM), that is an exciting technique for biophysical studies of single molecules, but its usefulness is limited by instrumental drift. We dramatically reduced positional drift by smear RBC to fix and thereby passivly stabilize the slide and the surface. However, there have some probably issuse shown in that. Because of smear destroy the phsical mechanical forece. Previous report presented fixation ability of six common fixation solutions, including 2.5% glutaraldehyde, 10% formalin, 4% paraformaldehyde, methanol/acetone (1:1), and ethanol/acetic acid (3:1), Poly-L-Lysine solution were evaluated by using atomic force microscopy in the much of publish work, unfortunately, that that did not stable repeat in the process. In addition, except for sample variation, the technic stability should be enhancement. Co-PI Prof Ho Lab will persisent to solve the problem. Ongoing study we will concentrate in cell menbrance structure image in cell biology field and animal study as well as to persistent cooperation with AFM information. |
| Appendix |
