Development of Continuous Catalytic Oxidative Processes for ive Conversion Valorization of Lignocellulosic Compounds to Non-toxic Antibacterial Sponge
- Publication Date: 2021-02-09
| Execution Methods | This research project is mainly to design and develop heterogeneous catalysts, aiming to develop filter-type copper-containing and TEMPO composite materials (as shown in Fig. 1) and apply them to the continuous-flow oxidation reaction of vanillyl alcohol, with high efficiency, high selectivity conversion rate, and easy product separation. The catalyst is easy to be recycled and reused. The converted vanillin can further utilize its antibacterial properties and special functional groups as hydroxyl monomers. Polyurethane (PU) is widely used and the foam has a market of 37.8 billion U.S. dollars in 2020. The hydroxyl groups of vanillin can react with isocyanates to produce urethane linkages. Vanillin aromatic ring increases material properties. Castor oil and its glycerides can be used as biomass polyols and solvent of vanillin. Vanillin-based PU foam can be synthesized via an environmentally friendly process.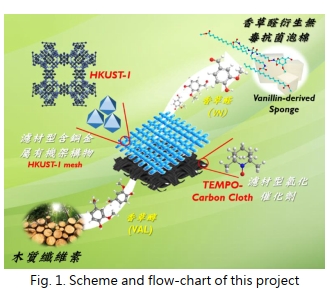 |
| Performance Evaluation | In addition, for the conversion of lignocellulosic waste-derived compounds with high efficiency, a heterogeneous sandwich-type catalytic system was further developed, which combined HKUST-1 mesh and TEMPO grafted on carbon cloth as a heterogeneous catalytic system (as shown in Fig. 2), which can be used at 120 °C. 60 minutes to achieve 100% conversion, 100% selectivity, and 100% vanillin yield.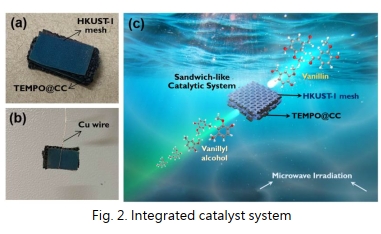 Vanillin-based PU foam (as shown in Fig. 3): The addition of vanillin reduces the foam density from 70.6 to 84.3 kg/m3. The compressive strength is controlled from 8.5 to 166.4 kPa, and the weight retention rate of solvent resistance is above 95%.  The antibacterial efficiency against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus reached 84.4 and 95.7 % (as shown in Fig. 4). 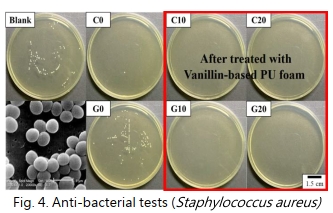 |
| Conclusion & Suggestion | This project is honored and grateful to receive the support of Enable Center and Professor Tu, to explore the concept of this project, and to take a step forward in the realization of this technology. In this year's results of this project, filter-type copper-containing and TEMPO composite materials have been successfully developed and applied to the continuous flow oxidation reaction of vanillyl alcohol. Low-density Vanillin-based foams with flexible or stiff properties have been successfully developed and high performance. Our team has samples for manufacturers or other institution to observe. In the future, it can be promoted and cooperated to enlarge the process to optimize product conditions. |
| Appendix |
